Cube Root
Definition of Cube Root
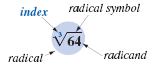
To indicate a cube root, we use the same radical symbol we used for
square roots, but we write a small 3 just above the
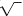 on the radical
symbol to indicate a cube root. The small 3 is called the index of the
radical. on the radical
symbol to indicate a cube root. The small 3 is called the index of the
radical.
For example, the cube root of 64 is written
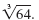
Definition —
Cube Root
The cube root of a real number, a, is written
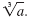 If b is a real number and b3
= a, then If b is a real number and b3
= a, then
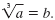
Example:
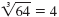 because 43
= 64. because 43
= 64.
Here are some examples:
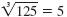 because 53
= 5 · 5 · 5
= 125 because 53
= 5 · 5 · 5
= 125
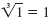 because 13
= 1 · 1 · 1
= 1. because 13
= 1 · 1 · 1
= 1.
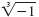 =
1 because (-1)3 = (-1)(-1)(-1) = -1. =
1 because (-1)3 = (-1)(-1)(-1) = -1.
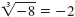 because (-2)3
= (-2)(-2)(-2) = -8. because (-2)3
= (-2)(-2)(-2) = -8.
Note:
To find the cube root of a number, we
reverse the operation of cubing.
For example, to find
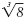 we ask “What
number cubed is 8?â€. we ask “What
number cubed is 8?â€.
The answer is 2.
Therefore,
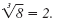
The last two examples show that a cube root, unlike a square root, can
have a negative radicand.
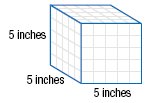
We can use geometry to provide a visual interpretation of a cube root.
For example, suppose a cube has a volume of 125 cubic inches. The length
of each side is the cube root of the volume.
That is,
the length of a side of the cube =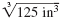 = 5 in. = 5 in.
A perfect cube is a number that has a rational cube root.
For example, 125 is a perfect cube because 53 = 125.
As we work with cube roots, we will find it useful to recognize perfect
cubes and their cube roots.
Now we will summarize the relationship between cubes and cube roots.
Property —
Cubes and Cube Roots
English Cubing and taking a cube root “undo†each other.
Algebra If a is a real number, then
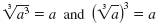
Example
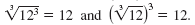
Note:
Unlike square roots, there are no
“principal†cube roots.
The sign of a cube root depends on the
sign of its radicand.
| Perfect Squares |
Principal Square Roots |
| 03 = 0 |
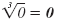 |
| 13 = 1 |
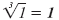 |
| 23 = 4 |
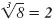 |
| 33 = 9 |
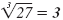 |
| 43 = 16 |
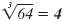 |
| 53 = 25 |
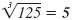 |
| 63 = 36 |
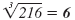 |
| 73 = 49 |
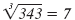 |
| 83 = 64 |
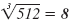 |
| 93 = 81 |
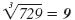 |
| 103 = 100 |
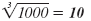 |
 |
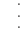 |
Property — Cubes and Cube Roots
English Cubing and taking a cube root “undo†each other.
Algebra If a is a real number, then
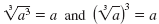
Example
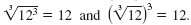
|