Dividing by Decimals
The following algorithm can be used to divide one decimal by
another decimal.
Division Algorithm for Decimals
To divide one decimal by another, use the following two steps.
1. Move the decimal points of both divisor and dividend to the
right the same number of places, until the divisor is a whole
number. This may require adding zeros to the end of the dividend.
2. Carry out the division as with whole numbers.
3. Place the decimal point in the quotient directly above the
decimal point in the dividend.
Example 1
Divide 14.292 by 0.12.
Solution
Begin by writing the problem in long-division form.
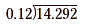
Next, move the decimal points of both divisor and dividend to
the right the same number of steps until the divisor becomes a
whole number. In this problem, it is necessary to move each
decimal point two places to the right.
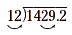
Now we can carry out the division in the usual way.
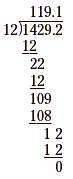
The quotient is 119.1.
Example 2
Divide 346.5 by 0.25.
Solution
Write the problem in long-division form.
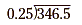
Next, move the decimal point the same number of places to the
right in both divisor and dividend so that the divisor becomes a
whole number. For the divisor to be a whole number, we must move
its decimal point two places to the right. Therefore we must add
a zero to the end of the dividend 346.5 so its decimal point can
also be moved two places to the right.
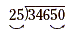
Now, we can carry out the division.
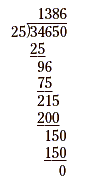
The quotient is 1,386.
|